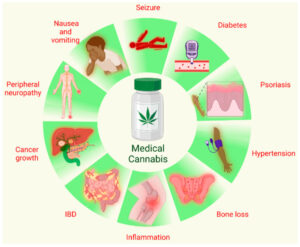
Cannabis has been used for centuries for various medicinal purposes . Recently, synthetic cannabinoids have been the primary source of medicinal Cannabis, and studies have found that THC is the primary source of adverse events. Unlike medical cannabis, recreational cannabis generally has a much higher THC content that can produce psychoactive effects. However, cannabinoids in combination (THC: CBD) may have the potential to be an alternative to opioids for chronic pain treatment. CBD can mitigate some of the responses caused by THC. Many studies have highlighted the presence of endocannabinoids (ECBs) and cannabinoid receptors (CBRs) within bone and joint tissues, underscoring their significant roles in bone metabolism and inflammation. Clinical investigations utilizing cannabinoid-based treatments in animal models have demonstrated the potential of cannabinoids to mitigate osteoarthritis (OA) progression, prevent osteoporosis (OP), and enhance fracture healing. These findings underscore the promising therapeutic prospects of CBD in addressing various human bone-related ailments. Future research is also needed to ascertain the potential involvement and role of endocannabinoids, endocannabinoid-like terpenes, and cannabinoid receptors in reducing systemic inflammatory responses.
There are over 100 cannabinoids, each with potential benefits that remain to be discovered. Some other areas of interest regarding treatment with cannabinoids include epilepsy, psychotic disorders, anxiety, and sleep disorders. Data shows acute CBD administration decreases experimentally induced anxiety in healthy humans . CBD is now available as an FDA-approved drug (Epidiolex®) for use as an anticonvulsant for refractory epilepsy (Dravet syndrome or Lennox–Gastaut syndrome), particularly in the pediatric population. Cannabis/cannabinoids may also help treat opioid addiction. Dronabinol, a synthetic THC drug, may help treat opioid withdrawal symptoms.
Medical cannabis expanded research is essential for enhancing our understanding of cannabinoids and their intricate interactions with the immune system during a pathogenic insult and other immune system disorders. Collectively, emerging evidence suggests that cannabinoids may hold great promise as innovative, relatively safe, and effective anti-inflammatory agents.